Even in conditions when Japanese persons are fairly constructive that one thing is true, they sometimes maintain again on expressing claims. Much like how one may use a layer of wrapping paper to cover what is admittedly inside a package deal, when talking Japanese, Japanese audio system recurrently encase their assertions in language that suggests they don’t seem to be positive about it. To swimsuit this social custom, Japanese provides quite a lot of grammatical phrases for various levels of certainty.
For instance, take into account a situation the place you arrive at work within the morning, and a coworker asks you whether or not you left a doc on her desk final night time. You didn’t try this, however you consider one other coworker, Tanaka-san, might have. That is what you may say:
- 田中さん[かな / かも / な気がする / だと思う]。
- It may be Tanaka-san.
These 4 phrases are introduced so as of diploma of certainty: from least sure to most sure. Though 4 may look like sufficient, that is merely the tip of the iceberg. Japanese has much more related expressions, and understanding them is essential for talking the language in a extra Japanese-like method.
To help you in utilizing Japanese in a means that probably sounds extra Japanese, this text discusses these phrases so as of diploma of certainty. Are you able to study them? Perhaps? Maybe? Effectively, it appears you’re prepared, I suppose. So, let’s get the ball rolling!
Stipulations: This text assumes you already know hiragana and katakana. If you want to brush up, take a look at our Final Hiragana Information and Final Katakana Information.
Notes: This text concentrates extra on the subtleties of every time period, significantly in extraordinary talking or writing. Some expressions may not be applicable in formal writing, equivalent to tutorial writing, as formal writing tends to require a inflexible and assertive fashion typically.
A Huge Image Take a look at Diploma of Certainty Phrases
As talked about within the introduction, there are many methods to convey your assumptions in Japanese. All of those expressions are for “judgments” made in mild of the obtainable info. The knowledge of the judgment, nevertheless, may be completely different relying on how a lot info the speaker is aware of, and the way a lot they depend on it to make judgments, in addition to whether or not or not they reached their assumption subjectively or objectively.
To assist your understanding, this is a chart to indicate you a tough concept of the understanding stage and the way subjectivity or objectivity every time period sounds:
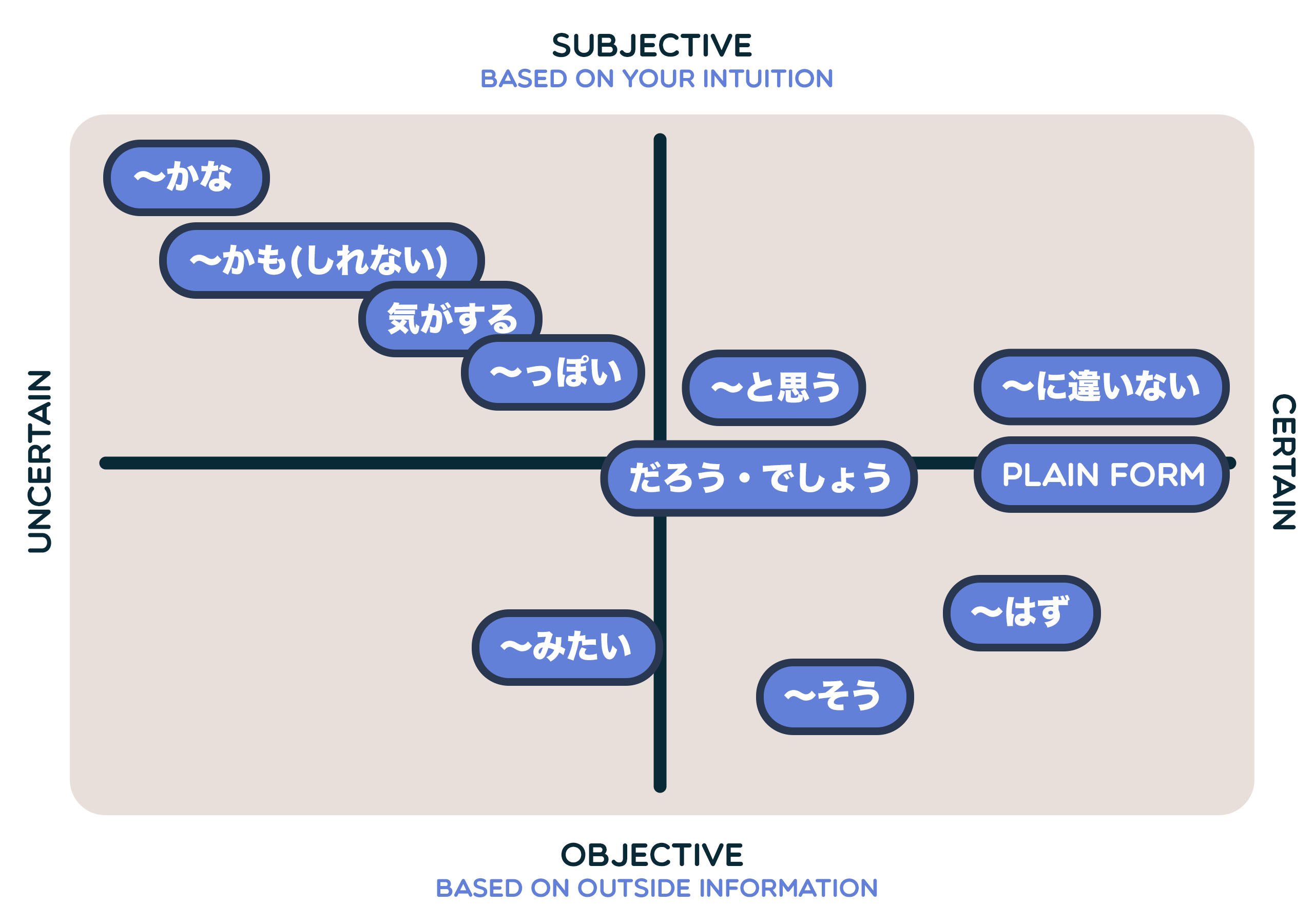
“Sure” and “unsure” ought to be fairly self-explanatory, however what do I imply by “subjective” or “goal”? Mainly, the extra “subjective” a time period is, the extra closely it is primarily based by yourself assumptions and instinct, whereas extra “goal” phrases rely a bit extra on exterior info or previous experiences along side your individual ideas.
Don’t fret in case you aren’t acquainted with these actual expressions but, although — we will go over them one after the other. Additionally, in case you really feel like this desk is lacking another phrases you already know, equivalent to 多分 (maybe) or きっと (certainly), relaxation assured that I will be masking them on this article as nicely, however in a separate part on the backside!
Expressions For Conveying a Low Stage of Certainty

To begin, let’s introduce expressions for conveying the bottom stage of certainty.
〜かな for “I Surprise…”
To precise your feeling of uncertainty, you need to use 〜かな. 〜かな is the equal of the English phrase “I’m wondering…” It is typically used with a notion or a hypothetical situation that has come to thoughts, and implies that you must take it with a pinch of salt.
For instance, in case you sneeze and also you marvel in case you have a chilly, you may stick 〜かな onto 風邪 (chilly) and say:
- 風邪かな。
- I’m wondering if I’ve a chilly.
Right here, 〜かな expresses that whilst you suppose you may need a chilly, you’re nonetheless uncertain and are questioning about it.
You too can connect かな to an extended sentence. For example, in case you marvel you could develop a fever, you would say:
- 熱が出るかな。
- I’m wondering if I am getting a fever.
In a means, 〜かな is kind of like asking your self a query, and thus it is thought of an off-the-cuff expression.
Once more, on this instance, 〜かな signifies that although you are afraid of getting a fever, you’re nonetheless uncertain and questioning about it.
Attributable to its nature, 〜かな lacks the well mannered type. To precise this kind of hypothesis when chatting with somebody in a well mannered method, you may as an alternative use 〜ですかね or 〜ますかね, or the extra formal 〜でしょうか(ね).
- 風邪[ですかね / でしょうか(ね)]。
- I’m wondering if I’ve a chilly.
(Actually: Do you suppose I’ve a chilly?)
- 熱[出ますかね / 出るでしょうか(ね)]。
- I’m wondering if I am creating a fever.
(Actually: Do you suppose I’ll develop a fever?)
Right here, です and ます are the marker for the politeness, か is the query particle, and ね is the confirmation-seeking particle. And, でしょう is likely one of the grammar factors used to precise hypothesis. Should you aren’t acquainted with them, take a look at the linked pages!
〜かもしれない for “Could” or “Would possibly”
〜かもしれない is the Japanese equal of “might” or “may.” It communicates the implication that one thing could also be true, however you are not utterly positive. In different phrases, it refers to your guess when there isn’t any concrete proof to assist it.
Let’s use the identical situation of you sneezing. As a substitute of “you marvel,” you suppose you may need a chilly. On this case, you need to use 〜かもしれない and say:
- 風邪かもしれない。
- I may need a chilly.
Right here, 〜かもしれない reveals that even in case you suspect that you just may need a chilly, you are not so positive. Should you’re very sure that your sneeze is being brought on by a chilly, you should not use 〜かもしれない.
Word that 〜かもしれない is commonly shortened to simply 〜かも in informal dialog, or in self-directed speech. So in case you now have some chills and are telling your member of the family that you just may develop a fever, it’s normal to drop しれない and say:
- 熱が出るかも。
- I could develop a fever.
Though it’s grammatically incorrect, some folks use 〜かも with です to lend a way of informal politeness. So in case you’re telling considered one of your superiors at work that you just’re pleasant with that you just may get a fever, you would say:
- 熱が出るかもです。
- I could develop a fever.
Nonetheless, you’ll use the right well mannered type, 〜かもしれません, in case you had been talking to a different senior worker with whom you will have a stiff, sq. relationship.
- 熱が出るかもしれません。
- I could develop a fever.
Alright, you have most likely had sufficient of 〜かもしれない expressions, so let’s transfer onto the subsequent expression!
〜気がする for “I Have A Feeling…”
〜気がする actually interprets to “have a sense,” and it is used to precise that you just aren’t sure however “you will have a sense that one thing may be the case.”
Since 〜気がする signifies that you’ve got a hunch about one thing, it sounds barely extra sure than 〜かな (I’m wondering) or 〜かもしれない (possibly/may). Nonetheless, the understanding stage of this expression remains to be low, as a result of it solely conveys a sense or guess primarily based on instinct, moderately than recognized info.
Let’s reuse the sneezing instance to see the way it works. After an enormous achoo, in case you intuitively suppose “Oh, I could have a chilly,” then you need to use 〜気がする and say:
- 風邪引いた気がする。
- I’ve a sense that I’ve a chilly.
Right here, 〜気がする expresses that whilst you get the sensation that you’ve got a chilly, there is no stable proof to assist this.
What in case you’ve been experiencing chills and wish to inform your boss that you just sense a fever is coming subsequent? On this circumstance, you need to use the well mannered 〜気がします and say:
- 熱が出そうな気がします。
- I’ve a sense that I could develop a fever.
As soon as extra, 〜気がします demonstrates that whilst you do have a sneaking suspicion that you could be get a fever, there is no concrete proof to again this up.
Alright, now that we have lined all of the low certainty expressions (except adverbs, which we’ll study later), let’s transfer on to the expressions for conveying a medium stage of certainty!
Expressions For Conveying a Medium Stage of Certainty

On this part, we’ll focus on expressions that convey a medium stage of certainty. You may use these if you suppose you will have some proof to assist your argument, however it stays a matter of conjecture, and you do not wish to assert ideas too strongly.
〜っぽい for “Like…,” “-ish,” or “It Appears…”
〜っぽい is a slang-ish suffix that expresses similarity, as in “(really feel) like…,” or “-ish” in English. For instance, in case you really feel like you will have a chilly, you may say:
- 風邪っぽい。
- I really feel like that I’ve a chilly.
And in case you’re feverish, and also you wish to report that to your boss, you may add the well mannered です and say:
- 熱っぽいです。
- I really feel feverish.
In these examples, 〜っぽい casually signifies that you’ve got some signs of a chilly or fever, however you do not essentially know in case you have an precise chilly or fever.
〜っぽい can even comply with the scenario during which you suppose it is doubtless true primarily based in your commentary, like:
- 風邪引いたっぽいです。
- It looks like I’ve a chilly.
On this case, 〜っぽい provides a way of ambiguity, like “Given the signs, it is doubtless I’ve a chilly, however it’s not a 100% positive factor.”
〜みたい for “Like…” or “It Appears…”
Much like 〜っぽい, 〜みたい is a suffix that expresses similarity or resemblance to one thing else. For example, in case you discover a yellow tomato that tastes like or appears to be like like a banana, you may say:
- バナナみたい。
- This is sort of a banana.
Relying on the scenario, using 〜みたい right here means that the yellow tomato has a taste or look that’s much like a banana.
In case you are curious, 〜みたい and 〜っぽい are comparable however distinct phrases. バナナみたい signifies that you suppose the tomato by some means resembles or is much like a banana, whereas バナナっぽい describes the tomato as having traits which might be type of like a banana.
Now, let’s change 〜っぽい with 〜みたい within the earlier instance 風邪引いたっぽい。(It looks like I’ve a chilly.), as in:
- 風邪引いたみたいです。
- It looks like I’ve a chilly.
〜みたい and 〜っぽい are certainly very related, and have the identical translation when used on this means. If I had been to be choosy, there are very small variations between the 2, although.
That’s, 〜みたい demonstrates your evaluation that your situation is akin to, if not the identical as having a chilly, whereas 〜っぽい reveals that, given your present circumstance, you get a sense that you’ve got a chilly.
Since 〜みたい signifies your evaluation, 風邪引いたみたいです is barely extra sure than 風邪引いたっぽいです. Nonetheless, because of the ambivalence added by 〜みたい, 風邪引いたみたいです nonetheless presents the message that you just’re conscious that you just most likely have a chilly, however are coming to phrases with it.
〜だろう/〜でしょう for “I Guess In all probability…”
In case your speculation about one thing relies on opinions and views with some justifications, you need to use the expression 〜だろう, or its well mannered type 〜でしょう, as in:
- 風邪だろうね。
- I assume that is most likely a chilly.
- 熱も出るでしょうね。
- I assume that they will most likely develop a fever, too.
Right here, 〜だろう/でしょう suggests that you’re making a private guess that you just consider might be true, whereas additionally suggesting that it’s supported by some type of proof.
These phrases are sometimes used whereas making an commentary and drawing your individual conclusions. Though it’s potential to make use of them to speak about your self, speaking about any individual or one thing else is much extra typical.
One other factor to remember is that だろう, or its abbreviation だろ, has an unrefined and rugged tone as-is. This rough-hewn side works nicely if you’re making an affirmative assertion about your guess in writing or in a proper speech. In extraordinary talking, nevertheless, it sounds robust and is commonly thought of masculine.
To melt the sound, the ultimate particle ね is usually used with it, simply as within the examples above 〜だろうね. Then again, 〜でしょう is a really well mannered expression and is favored in formal conditions. Including ね to it, as in 〜でしょうね, could make it sound female, although it is used throughout the gender spectrum in formal settings.
For these nuances, each 〜だろう and 〜でしょう may not all the time be the popular decisions in extraordinary conversations. As a substitute, many individuals select 〜と思う (I believe…) as an alternative to convey their assertion typically conditions. Talking of which, you may simply scroll right down to see how 〜と思う is used!
〜と思う for “I Suppose/Imagine…”
If you draw a conclusion primarily based on some proof, and really consider it is prone to be true, you need to use the expression 〜と思う (I believe/consider…), which is the mixture of the citation marker と and the verb 思う (to suppose).
For instance, in case you not solely sneezed however have chills and fatigue, you could say:
- 風邪引いたと思う。
- I believe that I’ve a chilly.
Right here, 〜と思う expresses that you’ve got some motive to again up your declare, and also you naturally got here to suppose that is most likely the case.
If you say 〜と思う, you’re merely expressing a thought, concept, or notion that simply occurred to you.
Should you’re questioning why the phrase “naturally” was inserted there, good eye! Japanese has two verbs for “suppose,” 思う and 考える. Between the 2, 思う refers to extra spontaneous pondering that bubbles up naturally “in your coronary heart,” whereas 考える is a extra methodical type of lively pondering, which we would say occurs “in your head.”
Now, let’s check out the above instance 風邪引いたと思う once more. Right here, the declare 風邪引いた (I caught/have a chilly) is a extremely satisfied sentence in and of itself (we’ll speak about this later too!), and what 〜と思う is doing is definitely softening the assertion by stating that it is the notion that naturally got here to you.
For that reason, the understanding of 〜と思う modifications relying on the sentence you connect it to. For instance, you may lower the extent of certainty by including 〜かな (I’m wondering) or 〜かも(しれない) (might/may) to the declare, like:
- 風邪引いた[かな / かも(しれない)]と思う。
- I believe that I could have a chilly.
On this case, 〜と思う softens the already obscure かな/かもしれない statements and makes them even much less sure. Then again, in case you add an adverb like 絶対 (undoubtedly), it turns into a robust conviction:
- 絶対風邪引いたと思う。
- I believe that I undoubtedly have a chilly.
However once more, simply saying 絶対 風邪引いた with out 〜と思う is stronger, and what 〜と思う is basically softening the robust assertion.
This occurs in English too, however as was talked about at first, Japanese folks sometimes reserve making assertions about one thing until they’re totally sure that it’s correct. Consequently, you hear 〜と思う, or 〜気がする (I’ve a sense…), used with many Japanese remarks to assist the speaker really feel comfy.
There was quite a bit on this part to soak up, huh? One closing level: the well mannered type of 思う is 思います. So, use 思います when telling your ideas to somebody with whom you want to converse to in a courteous method.
〜そう for “It Appears to be like/Appears Like…”
You too can use 〜そう if you consider that one thing is about to occur, somebody goes to do one thing, or some situation may be the case. For instance, in case you really feel such as you may develop a fever, you may mix it with the verb 出る and say:
- 熱が出そう。
- It appears to be like/looks like I am going to develop a fever.
〜そう will also be used with adjectives, too. For instance, in case your pal seen you were not feeling nicely, they may add 〜そう to an い-adjective しんどい and say:
- しんどそうだね。
- It appears to be like/looks like you are not feeling nicely.
As talked about earlier, 〜そう mainly interprets to “it appears to be like/looks like” in English. To place it one other means, you need to use this to easily describe what you suppose goes to occur, primarily based in your commentary of the current scenario.
Since 〜そう is mainly your report on what one thing “appears to be like/looks like” primarily based in your commentary, its certainty stage is barely increased than different expressions we have discovered to this point. Nonetheless, it nonetheless implies that you just aren’t sure, so when speaking about what’s seemingly about to occur, it typically goes nicely with 〜気がする, as in:
- 熱が出そうな気がする。
- I’ve a sense that I’ll seemingly develop a fever.
Word that since 〜そう is an expression that is depending on what you’re observing on the time you are talking, you can’t use it to elucidate an occasion that occurred prior to now.
Expressions For Conveying a Excessive Stage of Certainty

Now you have discovered all of the expressions for low and medium certainty, let’s transfer onto the high-certainty expressions.
〜はず for “Supposed To Be” or “Ought to Be”
Should you suppose that one thing is “supposed” to be or “ought to” be the case, foreseeably primarily based on goal, logical inference, the phrase 〜はず is available in play.
So in case you have sneezed, get some chills, and foresee {that a} fever is about to develop, you may say:
- 熱が出るはず。
- I ought to have a fever quickly.
Right here, 〜はず signifies that you just consider that it is extremely doubtless {that a} fever is coming quickly, and that perception relies on believable info.
And in case your assistant at work has some reminiscence of getting acetaminophen within the workplace cupboard, they may politely say:
- 薬があったはずです。
- There ought to be some medicine, if I keep in mind accurately.
On this instance, 〜はず means that they’ve a reminiscence of getting some drugs, if their reminiscence is correct.
In different phrases, 〜はず signifies an excellent diploma of certainty, however not 100%. It conveys that you just assume or consider that one thing is the case, however that you just’re conscious that it isn’t essentially so.
〜に違いない for “Should”
Like 〜はず, 〜に 違いない additionally denotes a excessive diploma of certainty, however it implies that your individual subjective judgment is concerned to succeed in the conclusion.
It is simpler to know the nuance of 〜に 違いない whereas evaluating it with 〜はず, so let’s carry again the sooner instance of you foreseeing an upcoming fever for comparability:
- 熱が出る[はず / に違いない]。
- I ought to have a fever quickly.
The implication right here could be very related, as each indicate that you have reached the idea that you’re extremely prone to have a fever quickly, given that you just at present have sneezes and chills.
〜に違いない sounds extra assured and robust than
〜はず, as a result of it conveys your private conviction on the conclusion.
The literal that means of 違いない is “no distinction” or “not a mistake.” It signifies that one thing is precisely what you suppose with none distinction or inaccuracy.
Thus, the literal that means of the phrase 〜に違いない is “I affirm that XYZ is correct and proper in each side,” which in fact conveys a really excessive diploma of certainty.
As you may see, what 〜に違いない implies is kind of inflexible. Therefore, it is extra of a literary expression than colloquial.
Though 〜はず and 〜に違いない had been interchangeable within the above instance, due to the slight distinction in nuance, they can not all the time be swapped. For example, attributable to its robust confidence, 〜に違いない can’t be used within the scenario the place you keep in mind one thing and it is extremely doubtless, however you are not 100% positive, like:
- 薬があった[はず(です) / ❌に違いない(です) / ❌に違いありません]。
- There ought to be some medicine, if I keep in mind accurately.
Should you use 〜に違いない, or its well mannered varieties 〜に違いないです or 〜に違いありません, within the above sentence, it might sound as in case you’re a detective or a some kind investigator — it is as in case you’re drawing conclusions in regards to the crime scene and asserting that some kind of medicine should have been current at a particular location prior to now.
The bottom of your declare may be both info, data, and even simply your intuition, however with all the data at your disposal, 〜に違いない expresses that you just can’t be sure that that would be the case.
For this connotation, detective characters in fiction might regularly make use of 〜に違いない in speech. Nonetheless, few folks wish to sound like detectives in actual life, so to say the identical factor, folks sometimes use 〜と思う, or its well mannered 〜と思うんです or 〜と思います, with an adverb, equivalent to 絶対 (undoubtedly):
- 絶対薬があった[と思う / と思うんです / と思います]。
- I certainly suppose that there was some medicine.
We’ll quickly undergo all of the adverbs for various ranges of certainty. Earlier than shifting on, nevertheless, we now have one final expression for top certainty to debate: the plain type.
Plain Type for “Realization” or “Conviction”
Nearly all of textbooks do not point out this, however when Japanese folks have simply realized one thing or are lastly satisfied that one thing is the case, they sometimes simply state it utilizing the phrase in its most simple “plain type.”
For instance, in case you sneeze and turn into satisfied that you’ve got a chilly, you may merely use the plain type and say:
- あ、風邪引いた(わ/な)。
- Oh, I’ve/bought a chilly.
Then, in case you really feel a chill approaching and are sure a fever will begin, you may say:
- うん、熱も出る(わ/な)。
- Yep, I am gonna have a fever.
Now suppose you genuinely begin feeling sick and have a excessive fever, and consider it is a flu. You may say:
- インフルエンザだ(わ/な)。
- This should be the flu.
These examples all have a plain type ending, both within the current or the previous tense. They will nonetheless take sentence-final particles which might be directed at your self, equivalent to わ (a judgment/sentiment marker) or な (a discovery marker). However even with out them, ending a sentence in a plain type sufficiently communicates your judgment or your discovery that one thing is true and that you’re assured in it.
You do not sometimes see the well mannered type on this use as a result of it is basically used for a self-directed realization or conviction. Nonetheless, you could use the well mannered type if you’re speaking to the viewers and talking in a well mannered method typically.
For example, in case you’re live-streaming your life and also you suppose you will have a fever the second you have sneezed, you would say:
- あ、風邪引きました(ね)。
- Oh, I’ve/bought a chilly.
Then, in case you really feel a chill and anticipate a fever approaching, you may say:
- うん、熱も出ます(ね)。
- Yep, I am gonna have a fever.
After which, you truly get actually sick and have turn into to suppose you will have the flu, you would say:
- インフルエンザです(ね)。
- This should be the flu.
As you may see within the examples, it is customary to make use of the particle ね on this scenario to solicit viewers settlement, as in “do you agree with my realization?”
Okay, now that we have gone by way of each expression for certainty, all that is left is to have a look at adverbs! Do not be alarmed; since you have already discovered a lot, I am going to solely briefly undergo every adverb. So, let’s carry on and get to the end line of this text collectively!
Adverbs For Completely different Ranges of Uncertainty

Along with the expressions discovered above, there are adverbs that denote varied levels of uncertainty. These adverbs regularly associate with different expressions you beforehand discovered, significantly with 思う, however the frequency of collocations relies on the phrase.
As promised, we cannot go into nice element about every adverb on this half; as an alternative, I am going to checklist the fundamental adverbs for various ranges of uncertainty (sure, there are literally greater than our checklist!😅), clarify the fundamental definition, and probably the most frequent collocation.
なんだか or なんか for “Considerably” or “By some means”
なんだか, or its extra colloquial informal model なんか, is an adverb for “considerably” or by some means.” This expression regularly goes with 〜気がする, as in:
- なん(だ)か熱が出そうな気がする。
- By some means I’ve a sense that I could develop a fever.
By including なん(だ)か to the sentence with 〜気がする, it may muddy up your already-murky intuitive guess and make it sound extra ambiguous.
もしかしたら for “Perhaps” or “Maybe”
もしかしたら is an adverb for “possibly” or “maybe,” and it is used when presuming one thing with a level of doubt. This expression is commonly used with 〜かも(しれない), as in:
- もしかしたら風邪引いたかもしれない。
- Perhaps I may need a chilly.
Different adverbs like もしかすると, ひょっとしたら, or ひょっとすると specific an identical nuance, however もしかしたら is the commonest.
多分 for “Perhaps,” “Maybe,” or “In all probability”
多分 is one other phrase for “possibly” or “maybe,” however its certainty stage is increased than もしかしたら and thus it mostly interprets as “most likely.”
Therefore, it is sometimes used with 〜だろう/でしょう or 〜と思う, as in:
- 多分風邪だろう。
- I assume it is most likely a chilly.
- 多分風邪引いたと思う。
- I believe I most likely have a chilly.
Nevertheless it will also be used with different expressions equivalent to 〜かな, 〜かも(しれない), or 〜はず.
恐らく for “In all probability”
恐らく additionally normally interprets to “most likely”, however its certainty stage is increased than 多分, and it is typically used to foretell a foul end result sooner or later. Additionally, the tone is extra formal and literary, so it is best fitted to formal conversations or in writing.
Due to this nuance, 恐らく is usually used with a really affirmative declare, accompanied by an inferring expression, equivalent to 〜だろう/でしょう or 〜と思う.
- 恐らく風邪だろう。
- I assume it is most likely a chilly.
- 恐らく風邪を引いたんだと思います。
- I believe I most likely have a chilly.
Within the above examples, the primary one seems like a written sentence or a blunt, self-directed thought, whereas the latter seems like a proper and well mannered speech.
きっと for “In all probability,” “Certainly,” or “Definitely”
きっと is one other adverb that would translate to “most likely,” however its certainty stage is way increased than 多分 or 恐らく and thus it mostly interprets to “certainly” or “definitely.”
Therefore, it may be used with an inferring expression, equivalent to 〜だろう/でしょう or 〜と思う, however it may additionally go nicely with the expressions like 〜はず or 〜に 違いない.
- きっと熱が出る[だろう / と思う]。
- I assume I am going to certainly develop a fever.
- きっと熱が出る[はず / に違いない]。
- I am positive I am going to develop a fever.
Word that きっと additionally has different implications relying on the context. For instance, the next sentence can have two readings relying on the context.
- きっと元気になるよ!
- I am positive [I’ll / you’ll / they’ll] be higher quickly.
Right here, in case you’re speaking about your self, it expresses willpower — you are decided to be higher quickly. When speaking about another person, alternatively, it may specific a robust need — you actually hope they wish to be higher quickly.
確実に or 絶対に for “Certainly,” “Definitely,” or “Completely”
確実に and 絶対に are the phrases for “certainly,” “definitely,” or “completely,” they usually specific a really excessive diploma of certainty.
Therefore, they can be utilized with an inferring expression, equivalent to equivalent to 〜だろう/でしょう or 〜と思う, but in addition go nicely with expressions like 〜はず, 〜に 違いない.
- [確実に / 絶対に]熱が出る[だろう / と思う]。
- I assume I am going to definitely develop a fever.
- [確実に / 絶対に]熱が出る[はず / に違いない]。
- I am positive I am going to definitely develop a fever.
They usually additionally go nicely with the plain type when expressing “realization” or “conviction.”
- これ[確実に / 絶対に]インフルエンザだ。
- I am sure that is the flu.
Between the 2, 確実に facilities on “certainty” primarily based on the target indisputable fact that there are not any errors, modifications, and many others., wheras 絶対に merely means “completely” and signifies being uncontested by something.
間違いなく for “Unmistakably” or “Undoubtedly”
One other adverb with a really excessive stage of certainty is 間違いなく, which signifies your unambiguous conviction and might translate “unmistakably” or “undoubtedly.”
It goes nicely with an inferring expression, equivalent to equivalent to 〜だろう/でしょう or 〜と思う or the plain type of a phrase that expresses “realization” or “conviction.”
- 間違いなく熱が出る[だろう / と思う]。
- I assume I am going to undoubtedly develop a fever.
- 間違いなく熱が出る(わ)。
- I am positive I am going to undoubtedly develop a fever.
Word that 間違いなく suggests that you’ve got given your judgment that one thing is undeniably true primarily based on some info you will have. Consequently, it carries a extra formal tone when in comparison with 確実に and 絶対に, although it may nonetheless be utilized in on a regular basis speech.
Fairly Probably the Conclusion
Whew! I do know that is lots of info to cowl, however don’t fret if you have not memorized all of it but. This web page could be a reference so that you can revisit time and again till you have bought all of it down.
Remember that the extent of certainty described on this article is simply an approximation, as the understanding conveyed can change relying on the context of the sentence, the one that makes use of the expression, and extra.
Lastly, like I discussed, word that this text is simply the tip of the iceberg; Japanese has tons of various methods for making statements much less sure or extra obscure, together with layering a number of the above expressions, utilizing double negatives, or extra. Nonetheless, hopefully it is a good place to begin for including extra nuance to your individual Japanese, or serving to you perceive the extent of certainty that somebody is attempting to precise. Try to observe what types of statements Japanese persons are making in actual life and the context during which they’re making these statements, and hopefully this kind of nuance will turn into second nature to you.
Footnotes:
